Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayMission critical data flows through your network. In today's world, the threat of cyber attacks is greater than it ever was. Every element in your network has to have protection to keep people out of where they shouldn't be.
With increased automation of remote monitoring systems, the impacts of these attacks on your elements could impact your critical operations. Because of that, it's vital that you make sure your data is confidential and that unauthorized people can't access it.
Let's take a look at the principal security features you should look for when evaluating an RTU for your remote sites.
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service technology - or simply RADIUS - is an industry-standard authentication method.
RADIUS provides a way to manage logins to many different types of equipment in one central location. It's architecture is fairly simple: many RADIUS devices connect to a central RADIUS server. Every time a device receives a login attempt (this usually means a username and password), it requests an authentication from the central RADIUS server.
Since all authentication requests are handled by the central server and not the devices themselves, updating user profiles and access permissions only has to be done in one place.
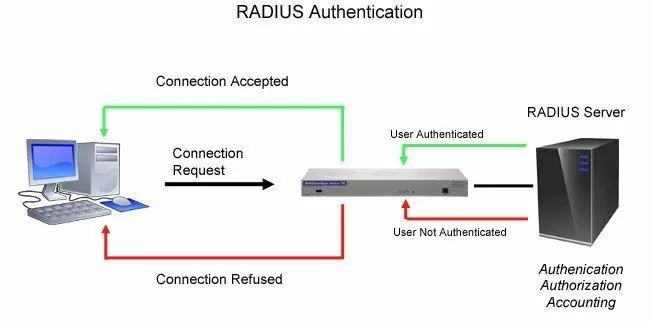
Many companies already have a RADIUS server in their network. It's a great way to centrally administer user access and passwords. RADIUS technology provides tougher authentication for government, military, and large private firms.
We're no different. Our RTUs have a long history of protecting access to your alarms.
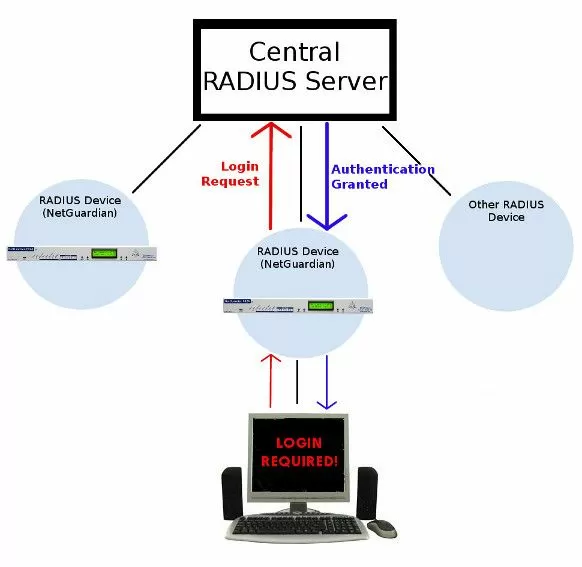
Many of our clients had RADIUS servers already running in their networks. We knew we had an opportunity to save them time and money, so we engineered RADIUS into our NetGuardian RTUs.
With the ability to pass NetGuardian login attempts to your RADIUS server, you gain several key security advantages:
Virtually unlimited users
With RADIUS, the number of user logins you can support is huge. Running out of user logins is almost impossible.
Centralized management
You'll also be able to manage your logins from your central RADIUS server. This means that you'll never have to worry about updating any single remote. If an employee leaves your company, you can revoke their access rights very easily.Integration with enterprise management
When all your RTUs use the same RADIUS authentication method as your other important gear, you drastically reduce the complexity of managing your equipment. It's easier to manage a single umbrella than it is to keep track of multiple unrelated systems.A good example of one of our RTUs that supports RADIUS is the NetGuardian 832A.
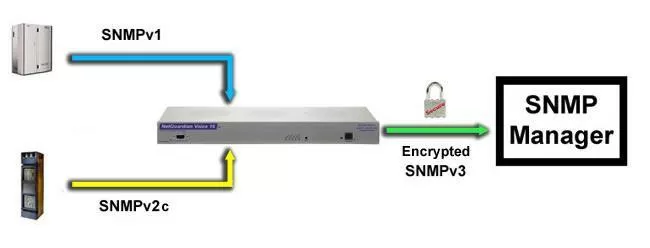
If you have the ability to choose which SNMP versions (SNMP v1, v2c, or v3) that you're going to use, choose to allow v3 access only. By doing this, you require all users and SNMP managers to use v3's enhanced security. In cases where security is less of a concern, it's okay to choose to allow all SNMP versions.
SNMPv3 is the most secure version of SNMP. An example of an RTU that supports this version is the NetGuardian 832A - which also encrypts its messages with CBC-DES encryption, a part of the Universal Security Model.
The NetGuardian 832A's ability to provide security is enhanced by its support of up to four v3 user profiles. Each user is assigned a unique set of security parameters, including authentication and/or privileged access. Authentication can be based on the MD5 or SHA algorithm. With either option, messages may be encrypted using DES 56-bit encryption based on CBC-DES, which allows for maximum security and flexibility.
The encrypted data appears scrambled if it's hacked, making it unreadable by anyone but the intended recipient.
This form of encryption makes SNMPv3 your best form of protection when routing SNMP messages over the internet. This is key if your company requires high levels of security, authorization, and access control.
Almost every day, you hear about a new computer virus or web browser security hole. And now these dangers aren't just for ordinary PCs, but also for any network equipment that supports a web interface.
The reason for that is that most web-based communication is not encrypted (although this is changing each day). Most of the time, this isn't a problem - there isn't much of a security threat if you're just reading the news. However, when it comes to the web interface of your RTU or alarm master, you've got critical alarm information - and access to control relays as well - that you need to protect. If working at a government or other security-conscious organization, then this is especially true.
Network experts are growing concerned that fundamental network equipment might be vulnerable to Internet-based attacks. One of the best practice standards is to secure your network equipment from open Internet access.
To secure your alarm monitoring web interfaces, make sure to go with an RTU that is available with HTTPS/SSL encryption - also known as Secure Web Interface.
I strongly recommend RTUs featuring an HTTPS software module if you usually connect to your remotes from your home. As well as if you work for a company that has security procedures for accessing equipment over IP.
The Secure Web Interface is the ideal alarm monitoring interface for on-call technicians who need to view alarm details from home, technicians who need to verify alarms and corrections from remote sites, also for supervisors who need to check network statuses from their desks or from the road.
DPS remotes have numerous security features, but the HTTPS software module gives you an added layer of security. This feature is available not only on our RTUs, but on our alarm master - the T/Mon - as well.
But how does HTTPS works?
This software module supports Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer, the industry-standard secure web protocol for online sales and financial transactions.
For instance, when a remote access user connects to the T/Mon using HTTPS, the T/Mon Web Server establishes a secure connection to the user's web browser. Data passing through the secure connection is encrypted, protecting the data from eavesdropping and "man in the middle" attacks.
If users connect to the unit from both inside and outside the company firewall, you can use HTTP and HTTPS connections at the same time. However, if you do, the best practice is to configure your router to block the HTTP port (typically port 80), so that no one outside your network can access unencrypted data.
Back to the T/Mon example, to connect to it over HTTPS, all you need to do is type "https://" followed by the IP address of the T/Mon system, into the address bar of your browser. The browser will show a security alert, and the you can view the T/Mon's security certificate.
When connected, the web browser window will display a lock icon to indicate a secure encrypted connection. The user may then log on and use the system normally, with complete security.
When you want to reduce your windshield time, having easy access to your equipment at your remote sites is great. However, how are you supposed to restrict this access to authorized personnel only?
One way to protect your gear is making sure your RTU has a security password - for users without the right password, the ports to your equipment should not even exist.
Our NetGuardian RTUs support two kinds of proxy connections, direct and indirect. Indirect connections are more secure than direct connections.
Indirect connections are essentially secure, because they're mediated by the NetGuardian interface, and the entire NetGuardian interface is protected by passwords. Users need a password to gain access to any NetGuardian function, and the unit administrator can define and limit the access privileges of each individual user.
Keep in mind that direct connections are not password protected. A direct connection is an ordinary unmediated Telnet link between your computer and a TCP port, bypassing the NetGuardian interface and its password security. A direct connection can be invoked straight from the command line by entering the Telnet command, the IP address of the NetGuardian, and the target's TCP port.
You can ensure the best possible security for your proxy connections by disabling direct proxy connections.
How can you disable direct proxy connections?
If you want a quick way to disable direct proxy connections, just set the TCP port to an uncommon value. This is, however, only security by obscurity. Which means that the TCP port is still available for a direct connection, if anyone can find it.
The best way to secure your RTU's proxy port is by using the remote's port definition interface to disable all TCP access.
Here's how it's done for a NetGuardian:
Connect to the NetGuardian
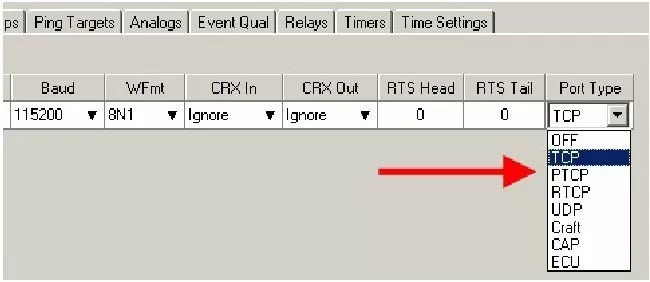
Using either NGEdit, the web interface, or the TTY interface, navigate to Port Definition.
Set the Port Type to Off
To disable TCP access, simply set the Port Type to Off. When set to Off, the port is no longer associated with a TCP socket, completely disabling the port from direct proxy connection.
In this era of increased security measures and diverse network topology, an increasing number of deployments require a second network interface.
So, another way to have an enhanced security is to find an RTU that has two separate NICs - Network Interface Cards. This allows you to connect your remote to two different networks and allows multiple users on separate networks to access the same unit. This also allows you to have redundant access in case one network goes down.
Again we can use the NetGuardian 832A as an example of an RTU that has a secondary NIC, permitting you to connect to two different networks.
It's also important to note that, from a security and segmentation point of view, both LANs can access the NetGuardian 832A, but they can't access each other. SNMP traps, FTP, web browsing and Telnet can be accessed from either NIC. Each LAN has its own status LEDs to facilitate setup and operation.
Other than the previous 5 principal security features that you should absolutely require on your RTU, DPS also has some other security features. Some of them are:
IP filtering
Sometimes a whitelist is better than a blacklist, right? With IP filtering, you can limit access to your monitoring system to specific IP address ranges. This can really cut down on your system's vulnerabilities.
Modem dial-back
Simple technology can become very powerful when it's used the right way. Devices that support modem dial-back can call you whenever they've been accessed. Under normal circumstances, you'll get a call only after you've made a change. If you get a call and you haven't been making any changes, then you'll know that someone else did.
Granular user-level privileges
If you have to give "all or nothing" access to your system users, you're forced to create unnecessarily security risks. It's much easier to give your personnel only as much access as they need to perform their jobs. In case of an incident, your list of internal suspects will be much shorter.
Passing ISS scanners
Our products are built on strong proprietary platforms, which means that they're less vulnerable during standard intrusion tests, such as ISS scanners.
Enforced "strong" passwords
If you let every member of your staff choose any password they like, you'll probably end up with lots of short, lowercase dictionary words. That's basically any hacker's dream scenario. With our products, you have the option to require a "strong" password - minimum length and mandatory character types.
Logging user activity
If an incident occurs, you need a log to refer to so you can find out what happened. Logging the user's ID for alarm acknowledgments and similar activities is a great obstacle against unauthorized activity.
Ability to assign unique ports for functions
Hackers most of the times depend on your usage of standard ports for certain kinds of traffic. Our products allow you to select a custom port for various jobs, making you immune to many "mass" attacks that only infiltrate through commonly used ports.
"Dark answer"
When an unauthorized user wants to gain access to your systems, they send various sorts of requests and measure the responses. If your system doesn't reply, a hacker's job gets way more difficult. With this feature activated, your DPS equipment will issue no apparent login prompt. Once you log in - because you know that the system is, in fact, listening for your username and password - the system responds normally.
Those features that I explained previously are just some of the ways our NetGuardians can help you securely manage your remote sites and your remote site equipment.
If you want more information about DPS RTUs, if you have questions about any security feature, or if you simply have a question about remote monitoring - don't hesitate to contact me.

Morgana Siggins
Morgana Siggins is a marketing writer, content creator, and documentation specialist at DPS Telecom. She has created over 200 blog articles and videos sharing her years of experience in the remote monitoring industry.