Check out our White Paper Series!
A complete library of helpful advice and survival guides for every aspect of system monitoring and control.
1-800-693-0351
Have a specific question? Ask our team of expert engineers and get a specific answer!
Sign up for the next DPS Factory Training!

Whether you're new to our equipment or you've used it for years, DPS factory training is the best way to get more from your monitoring.
Reserve Your Seat TodayIn the network monitoring world, you might be faced with the challenge to choose between SNMP and Syslog protocols when considering a remote monitoring solution.
Both SNMP and Syslog are used by network administrators for remote monitoring their facilities. They can provide very comparable monitoring information but the way they go about it is different. Learning about both protocols can help you decide which make more sense for your network and application.
Let's take a look at the main differences between Syslog and SNMP.
Syslog is a communications protocol that is used to send data logs of different degrees of severity to a central location for storage. Logs can then be accessed and analyzed in order to provide monitoring and troubleshooting.
Due to its flexibility and ease of use, this logging method has been around since the 1980s. The Syslog protocol has maintained its popularity because it can be supported by a wide variety of equipment.
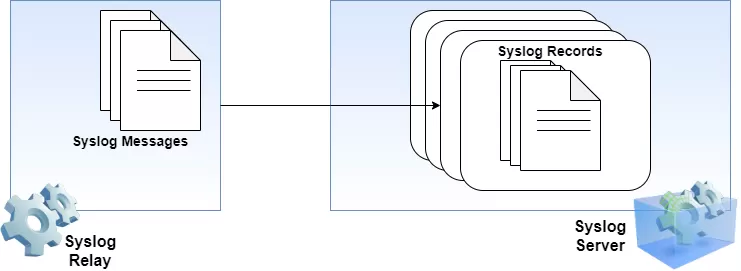
Its layered architecture is formed by three components: the network device that generates the logs, the Syslog relay that forwards the logs to a collector, and the Syslog collector (or server) that will receive and store the logs.
Syslog messages are triggered by events within a system. They are designed to alert you when an important event happens within a system that might be of interest to you. There are different levels of Syslog messages from Level-0 (Emergency messages) to Level-7 (Debugging messages).
The format of each log includes timestamps, host IP addresses, event message, severity, diagnostics, and more. Examples of logs can be configuration changes and authentication attempts.
Syslog messages follow a structured format defined by the syslog protocol (RFC 5424). Each message consists of a priority value (PRI), a header, structured data, and a message body.
The PRI encodes the facility (type of source) and severity (urgency level) of the message. The header includes a timestamp, hostname, application name, process ID, and message ID.
Optional structured data provides additional context in key-value pairs. The message body contains the actual log event description. This standardized format ensures syslog messages are easily parsed and understood by log management tools.
Here is an example of a syslog message:
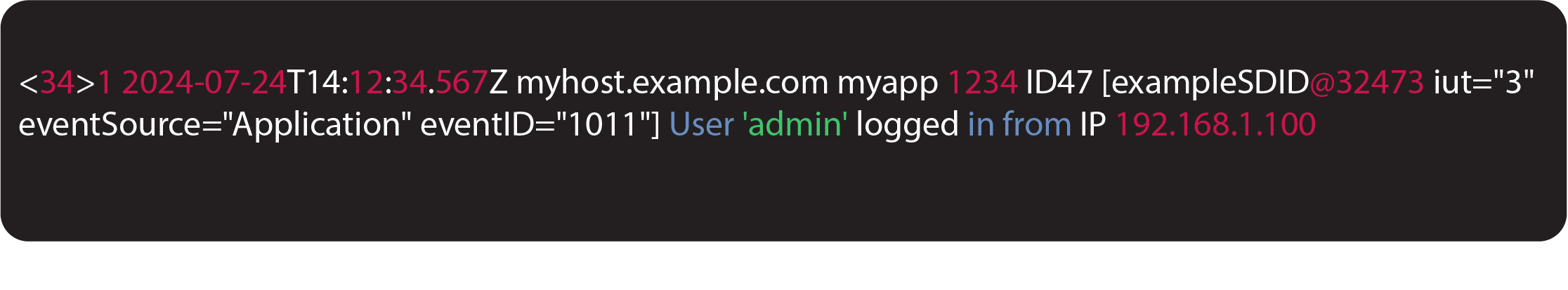
Here's a breakdown of the components in this syslog message:
Syslog is essential for application monitoring on a server as it provides centralized and standardized logging. It collects log messages from various applications into a single location. This simplifies log management and analysis. This centralization enables real-time monitoring which allows administrators to set up alerts for immediate notification of critical events or errors.
Syslog enhances security by logging authentication attempts and access controls. This creates a detailed audit trail for forensic analysis. It also tracks performance metrics and error messages, helping to identify performance bottlenecks and anomalies. Additionally, Syslog ensures compliance with regulatory standards by maintaining comprehensive records of application activities for auditing purposes.
Moreover, Syslog integrates seamlessly with other monitoring tools, offering a unified approach to server and application monitoring. By leveraging Syslog, administrators can improve performance, security, and compliance for their server environments.
Syslog is essential for network monitoring because it offers:
This standardization ensures network administrators can
Syslog is essential for network monitoring and analysis. It enables centralized logging from various network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls. This centralized approach allows for real-time monitoring of network activities. This real-time monitoring facilitates quick detection of anomalies and issues. By collecting logs from multiple sources, syslog helps in event correlation and analysis. These data logs aid in identifying patterns and potential security threats. It is crucial for security monitoring, performance monitoring, and troubleshooting by providing detailed logs that help diagnose and resolve issues efficiently.
Additionally, syslog supports compliance and auditing. Syslog maintains a comprehensive audit trail of network activities, ensuring regulatory adherence. It also enables proactive alerting and reporting based on specific log patterns. This increases network reliability and security. Overall, syslog significantly contributes to robust network management and security by providing comprehensive insights and centralized control.
Syslog enhances security by centralizing logging, ensuring data integrity, and using encryption for secure transmission. It enforces authentication and authorization to restrict log access. Syslog also maintains audit trails for forensic analysis and detects tampering with logs.
Syslog effectively supports real-time monitoring and alerting. This allows for quick responses to security incidents. Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems further strengthens security by allowing advanced analysis and threat detection. Through these measures, syslog ensures that log data is securely managed and analyzed. This supports an organization's overall security strategy.
Syslog can be effectively used for security, authorization, and auditing in a corporate network by providing a centralized logging mechanism. For security, it captures logs from firewalls, IDS/IPS systems, antivirus software, and network devices. This helps detect intrusions, malware, and unauthorized access attempts. In terms of authorization, syslog tracks user activity, monitors privilege escalations, and enforces access controls by logging events from authentication systems and applications. For auditing, syslog supports compliance reporting, change management, and incident investigation. Syslog does so by maintaining a comprehensive log of system activities and changes.
To implement syslog effectively, organizations should deploy a centralized log management system. Afterwards, define log retention policies and use log analysis tools for parsing and generating alerts. Maintaining the security of log transmission and storage through encryption and access controls is crucial. By doing so, organizations can enhance their security posture, enforce authorization policies, and maintain thorough audit trails. These contribute to a more secure and compliant IT environment.
Windows systems can implement syslog within the standard Event Log system by using third-party syslog agents like NXLog, Snare, or Syslog-NG. These agents collect Windows Event Logs and forward them to a syslog server. To set this up, install the chosen syslog agent on the Windows system. Afterwards, configure it to specify the log source and destination syslog server. For example, with NXLog, you would edit the "nxlog.conf" file to define the input (Windows Event Logs) and output (syslog server) settings. Then, restart the NXLog service to apply the configuration.
After configuration, verify that the Windows logs are being forwarded correctly to the syslog server. You can do this by checking the server's log entries and generating test events on the Windows system. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the syslog agent and configuration maintain continuous and accurate log forwarding. This enables centralized log management and enhances security, authorization, and auditing capabilities.
A syslog server is a centralized system that collects and manages log messages from various network devices and applications. Its main functions include
Syslog servers provide real-time monitoring and alerting. This helps detect and respond to security incidents quickly.
The servers uphold data integrity through encryption and access controls. Thry also support compliance and auditing by maintaining detailed records. They offer tools for generating reports and visualizing network trends. By carrying out these functions to centralize and secure log data, syslog servers enhance network management, security, and compliance.
SNMP is an application-layer protocol that allows for exchanging management information between network devices. This protocol allows information about equipment to be collected in a standard way even between different hardware and software types.
SNMP messages are transmitted between managers and agents.
The SNMP manager is a centralized platform to which agents feed information. It will provide you with an interface for your monitoring system and will send you notifications about conditions that require you to take corrective action.
The SNMP agents collect data from the equipment located at remote sites and send this information to the manager. Some agents can also send you notifications about alarms and, in small networks, having only managed agents make sense. However, if you have more than a handful number of agents, the cost-efficient way to maintain your visibility is to deploy a manager to provide a centralized monitoring interface.
In the SNMP definition is also important to know that the communication can be started by polls or trap messages.
Polls or GetRequests are the most common SNMP message that a manager sends out to ask for information. The recipient device will reply with the requested data. Trap messages are sent by the managed devices without a request from the manager. When a change of status happens, managed devices will proactively send out traps to inform about the condition.
SNMP allows for remote monitoring and control of SNMP-enabled devices on a network, while Syslog can be used for communicating log messages of different severities to network devices capable of supporting Syslog messages. This means that Syslog, different from SNMP, doesn't allow you to remotely control your network devices.
Logging messages is useful for debugging purposes and quick information, while SNMP traps are useful if you need a complete application that will collect, monitor, control and produce complete reports about your devices.
Another difference to keep in mind is that SNMP traps are real-time communication - as soon as a change of status happens the trap is sent. Syslog messages, on the other hand, can be queued so they will not necessarily be delivered as they occur.
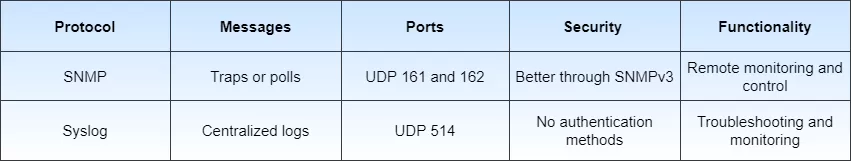
So, in a nutshell, the most important differences between SNMP and Syslog are:
Although there are many differences between these two protocols, we can also find some similarities between them. If you are curious to know, here are some of them:
There's no good or bad protocol. Choosing between SNMP and Syslog will depend solely on your unique network and its requirements.
Syslog works more as a troubleshooting tool and is used when logs are needed for an investigation. This protocol is generally used for quick historical events. SNMP, on the other hand, works on device-based events. This means that it provides real-time information and allows for better management.
In most cases and depending on the needs of your network, using a combination of both is the best solution.
Unfortunately, it is hard to find RTUs that can report Syslog messages to your Syslog server. That is because most RTUs use only telecom or SCADA protocols, such as SNMP. This is a common problem that can lead you to invest in two different monitoring systems that can't work together.
Having RTUs for your SNMP gear and other monitoring gear uniquely for your Syslog equipment is not practical. Not only this means that you'd have to come up with a bigger budget, but also you'd have to keep an eye on many different screens because your systems will not be integrated.
The best practice here is to find a remote monitoring system that can handle both protocols. As a vertically integrated manufacturer, we provide custom-fit monitoring devices that can solve this problem. We can redesign one of our existing devices or completely build a brand-new RTU that will match your network needs and reports messages to your current master station - either a Syslog or an SNMP one.
Reach out to us today and learn how you can get the best of both worlds.

Morgana Siggins
Morgana Siggins is a marketing writer, content creator, and documentation specialist at DPS Telecom. She has created over 200 blog articles and videos sharing her years of experience in the remote monitoring industry.